0:00
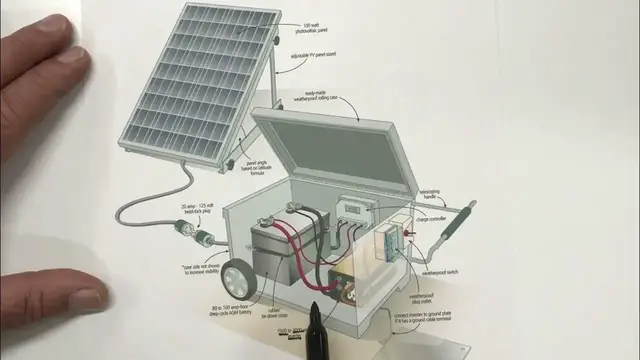
In this video I want to give you an overview of the solar generator I've designed
0:06
It's got different parts. This is the photovoltaic cell, the PV panel, and it captures energy from the sun and
0:15
converts it into electricity. Here we've got the cable that leads to the actual generator box
0:23
In this case that's a twist lock plug. There are different options for making this connection and I'll explain that later
0:29
The idea is to be able to remove or disconnect the solar panel from the rest of the unit
0:37
because you need to do that to be able to move things around. Now here we've got the battery
0:43
This is what stores the electrical energy from the PV panel. And over here is what's called the charge controller
0:51
It wouldn't do the battery any good if electricity from the photovoltaic panel just kept coming into the battery
0:59
unrestricted. We need something that monitors battery voltage and controls the charge going to the
1:07
battery, and that's the job of the charge controller. Now, you could use the electricity from this
1:14
battery directly. In most cases, this will be a 12-volt supply of direct current power. But if you
1:21
wanted to use appliances that require AC power, which is really a good idea, you also want
1:28
something called an inverter. That's what's shown here. It comes in different sizes, and I'll be talking
1:33
a lot about that later and making specific recommendations for the kind of inverter that going to work well for you Now with an inverter in place to make the most use of that power you going to want to have some sort of an outlet
1:46
In this case, it's a shielded waterproof outlet and a switch that can turn that power on and off
1:55
In some cases, you also need a ground plate, like you see here, which would be removable
2:01
Depends on the inverter you're using. but this is the overview of the system and it fits into a box that's portable you can either build this out of plywood
2:11
I do make specific recommendations for the kind of rolling case that makes sense in this case but
2:18
before I go on to other content in the video ebook I want to show you the schematic drawing of how all
2:28
of these things are wired together now this is the same Sort of arrangement that I just showed you, but this is the schematic drawing so it shows how things are wired up
2:40
So in this case we have our 100 watt photovoltaic panel. That's a pretty standard size and it'll work well for the solar generator
2:48
We've got some sunlight landing on the panel and it's generating power
2:55
This case it's it's 12 volts in reality. It's not actually 12 volts. It's gonna vary depending on the intensity of the sun but
3:03
for these purposes, we'll just call it 12 volts. And that power is supplied to the charge controller
3:11
In this case through some 12 flex cable So number 12 that refers to the thickness of the conductor so 12 gauge and 2 refers to the fact that there are two conductors sheathed together in the same cable
3:29
And it's a flex cable, so it's got a rubber insulation on the outside and it bends very easily
3:34
So the PV panel connects to the charge controller. And the charge controller decides how much power is going to the battery
3:43
So here we have the positive terminal from the charge controller, the negative terminal going to the negative side of the battery
3:52
And of course, if you want to build a high quality unit, you want to put fuses in lots of places
3:58
So we have this connection fused in case something goes wrong, a short or something goes wrong with the charge controller
4:05
That fuse is going to protect your circuitry. So that's the incoming supply
4:11
so incoming from the PV cell to the battery. Now, the outgoing supply is a separate system
4:20
and it takes much, much thicker wires because the rate of charge in amps coming in from the panel
4:31
to the battery is relatively small. But depending on how much power you're demanding from your inverter
4:39
the current can be extreme. extremely high. So it takes thick wires. There's more details about this in the video ebook
4:48
but it going to be anywhere from from number one to four aught cable That a designation of the diameter And of course you going to want a fuse in here too The fuses are always directly related to the cable size because the main job of the fuse is to protect the cable
5:07
from having too much current flowing through it and overheating and maybe even melting. So
5:12
look later for ratings of the kinds of fuses you need to match the cable. So lots of current
5:21
coming out here, 12 volts from the battery. And the job of the inverter is to convert that to 120 volts, alternating current
5:34
It's the kind of thing that you might use with a kettle or a microwave or some kinds of chargers as well
5:42
And the inverter can either be a pure sine wave inverter, which makes the pure purest power
5:51
or less expensive models that don't make power as pure. And I'll explain more about that later in the course
6:01
But this is how everything is wired together in a theoretical sense, in a schematic sense
6:08
And your job, as a builder of one of these things, is to acquire the different parts you need and then to put them all together in that case
6:19
So you've got a supply of power. that you can continue using forever
6:24
It's not like a regular portable gas power generator. In a long-term power failure
6:29
you're not going to be able to get any gas and oil for that thing, but this can keep on going for years
6:35
So that's what this solar generator thing is all about, long-term power security